TL;DR
We give a comprehensive study of the advanced technique for remote sensing representation learning including several latest self-supervised learning and fine-tuning for downstream tasks technique and self-supervised learning including like contrastive learning, a masked autoencoder style, JEPA style and so on.
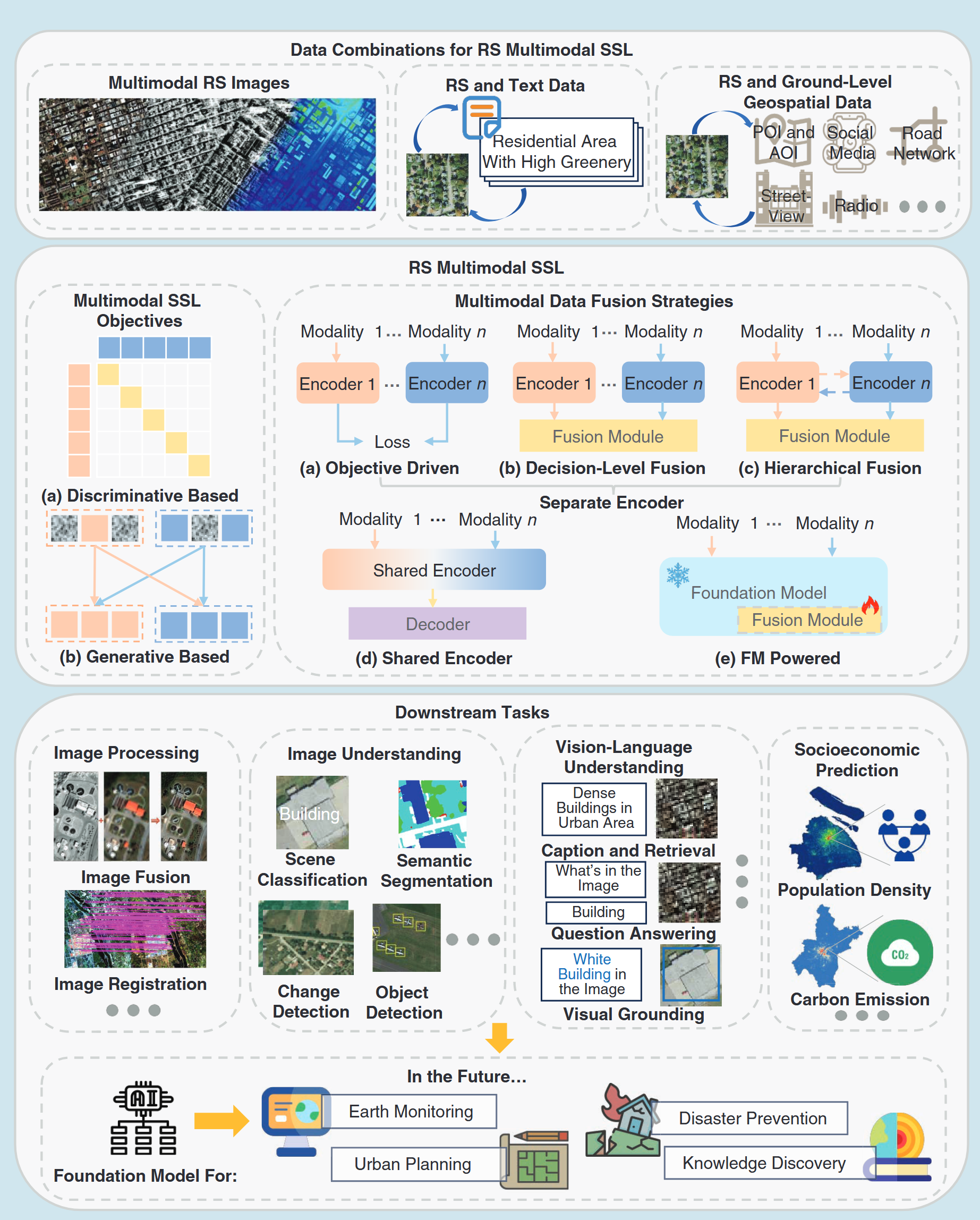
Introduction
The success of foundation models, especially large language models (LLMs), has demonstrated the effectiveness of Self-Supervised Pre-training plus Domain Supervised Fine-tuning strategy. This paradigm has been successfully adopted in the remote sensing domain, achieving remarkable results. Remote sensing data is often considered a distinct modality in machine learning due to its unique spatio-temporal characteristics, varying resolutions, and diverse sensor types [Rolf et al., 2024].

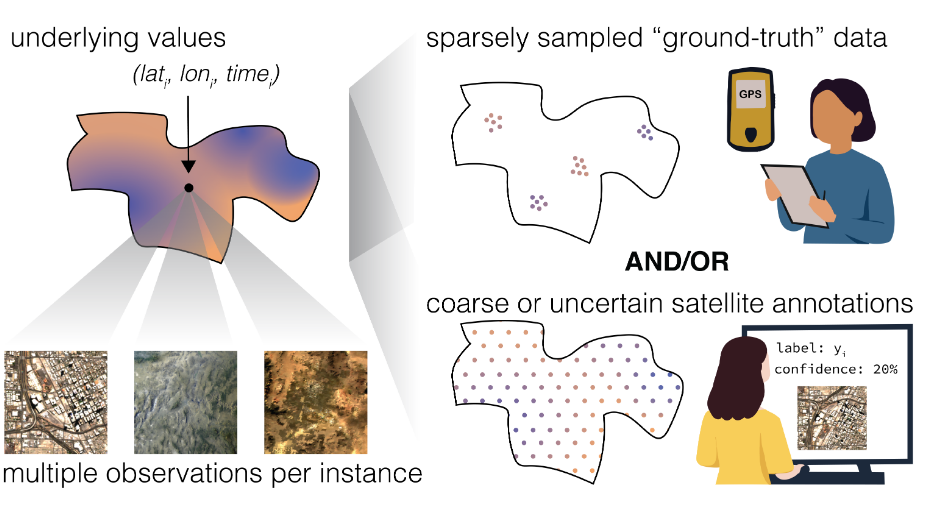
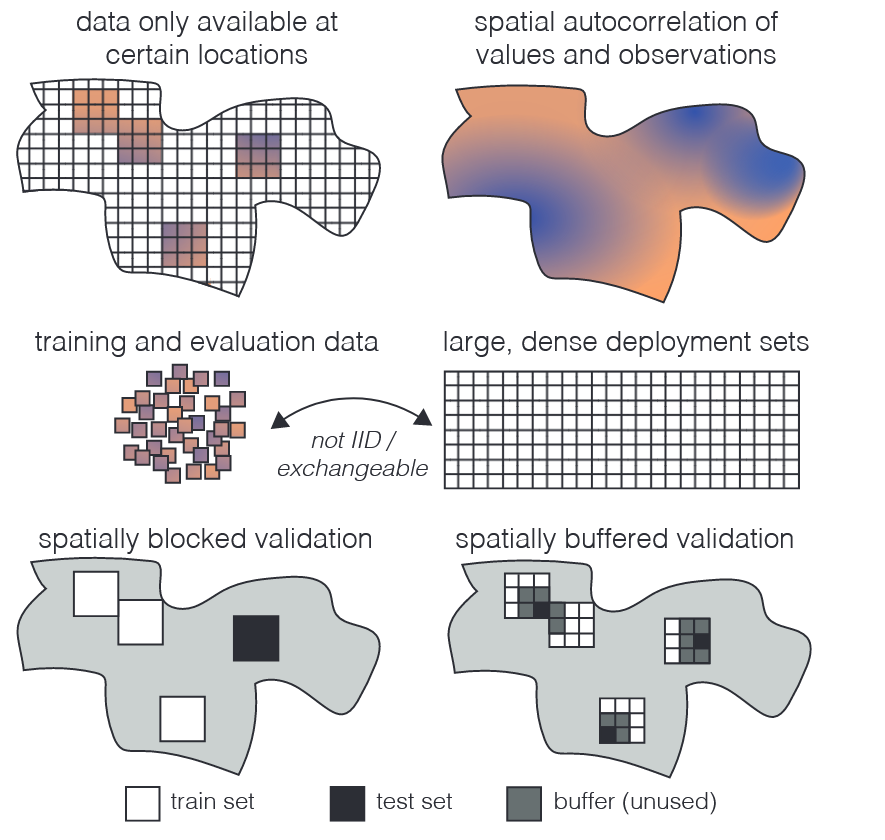
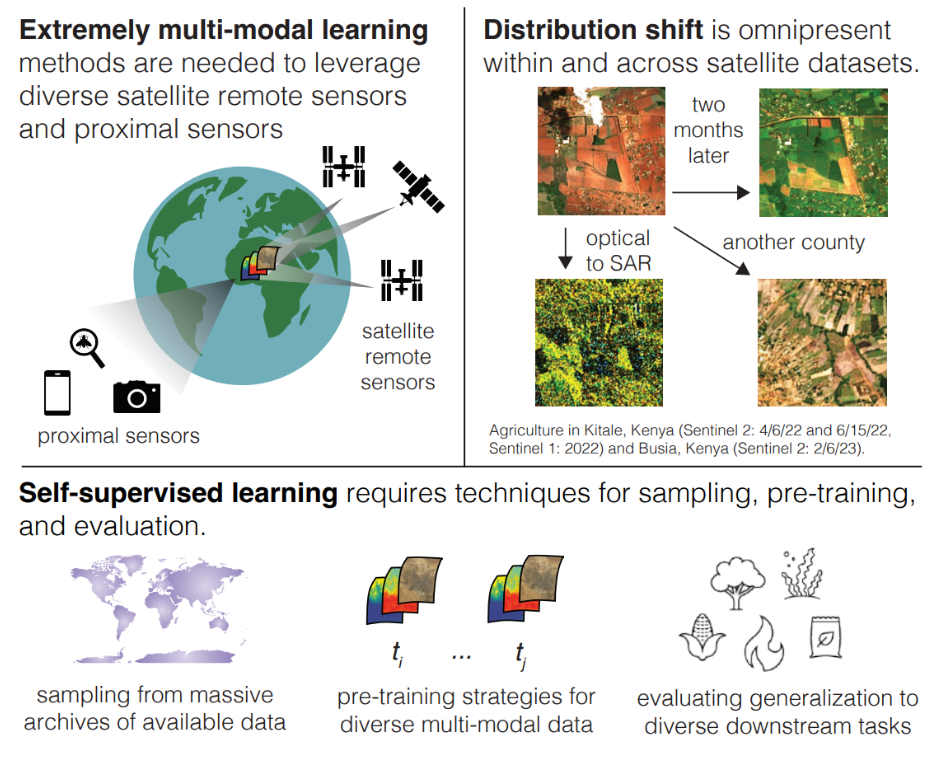
Review: Self-Supervised Learning in Remote Sensing (2020-2025)
We review the latest novel papers that adopt self-supervised learning in remote sensing images.
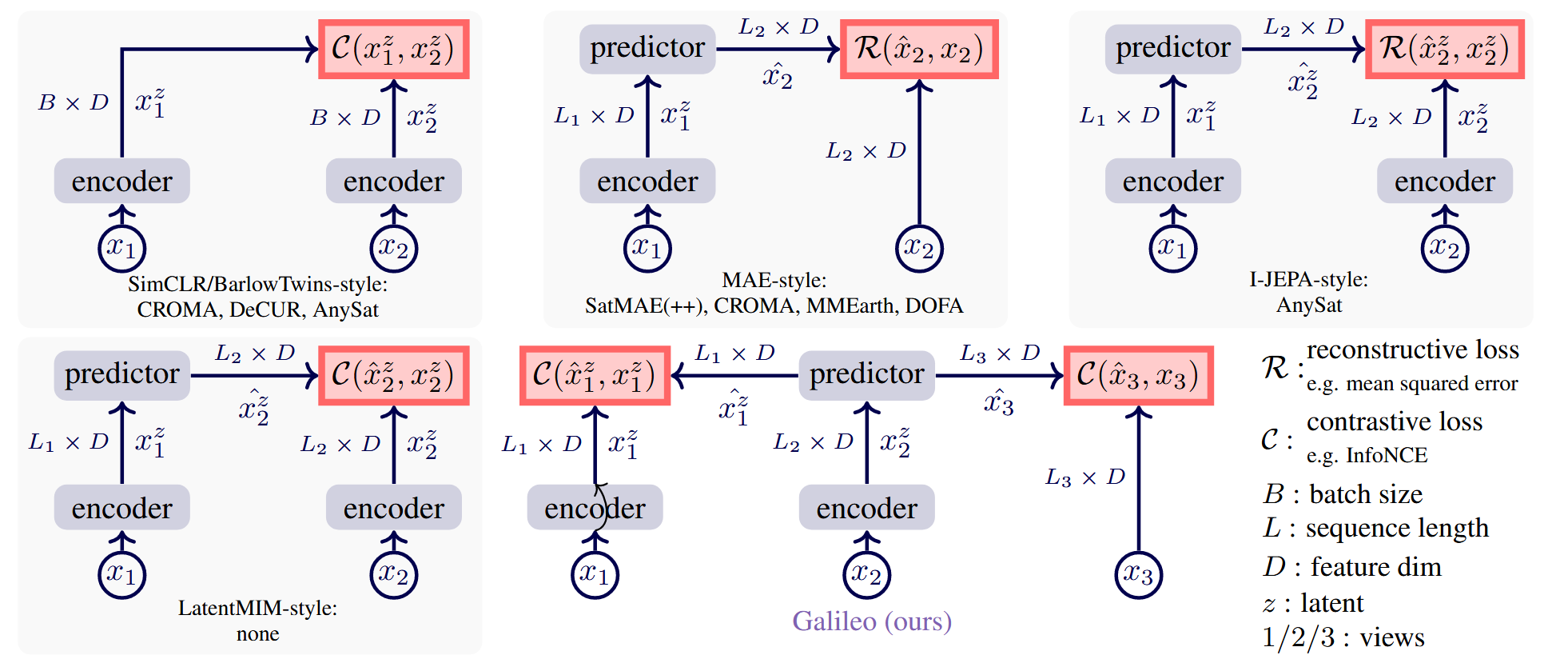
1. Contrastive Learning
1.1 CLIP-style Contrastive Learning

Adoption in Remote Sensing:
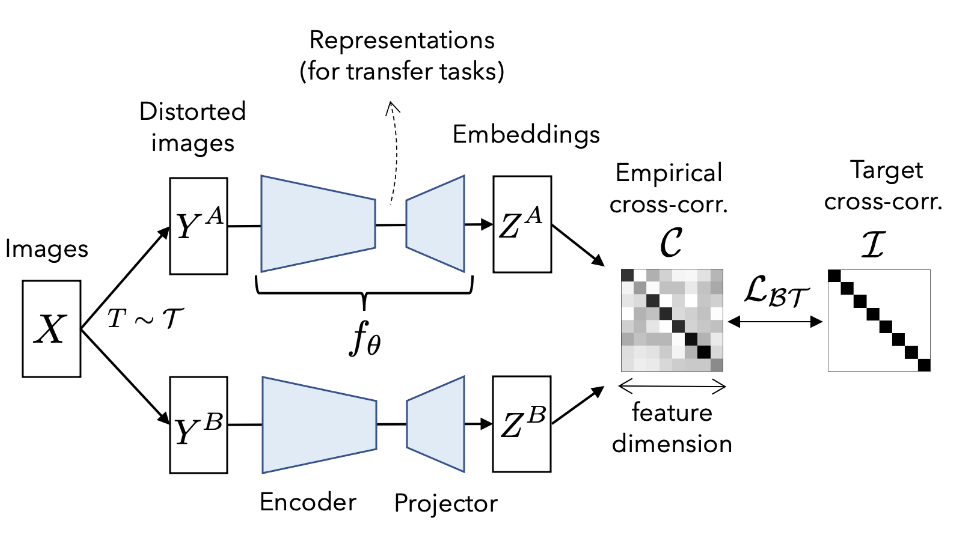
1.2 Barlow Twins-style Contrastive Learning
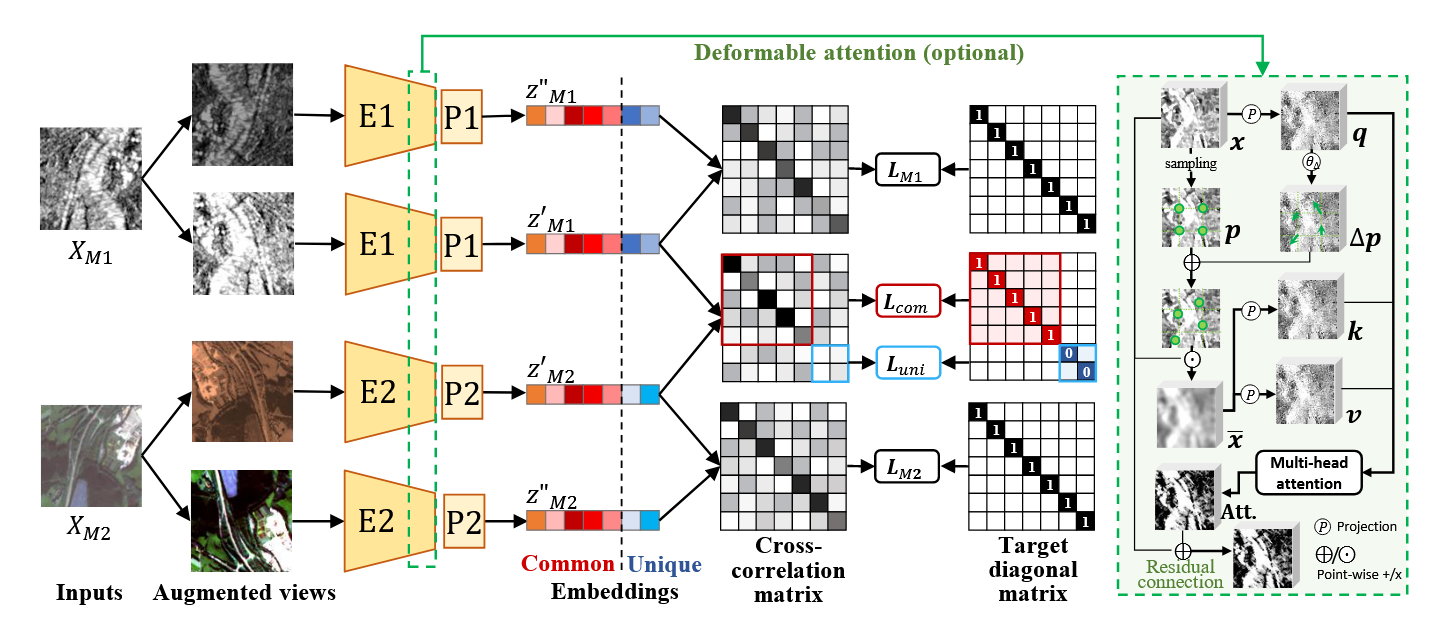
📐 Detailed Loss Definition of DeCUR (Click to expand)
Cross-Correlation Matrix
Given two embedding vectors \( Z^A, Z^B \in \mathbb{R}^K \), the cross-correlation matrix \( \mathcal{C} \) between them is formulated as:
$$ \mathcal{C}_{ij} = \frac{\sum_b z_{b,i}^A z_{b,j}^B}{\sqrt{\sum_b (z_{b,i}^A)^2} \sqrt{\sum_b (z_{b,j}^B)^2}} $$where \( b \) indexes batch samples, and \( i, j \) index the dimension of the embedding vectors. \( \mathcal{C} \in \mathbb{R}^{K \times K} \) is a square matrix with values ranging from -1 to 1.
Cross-Modal Representation Decoupling
The correlation matrix \( \mathcal{C} \) is calculated between two embeddings from different modalities, such as \( Z_{M1}' \) and \( Z_{M2}' \). The total embedding dimension \( K \) is separated into \( K_c \) and \( K_u \) with \( K_c + K_u = K \) to store common and unique representations, respectively.
Cross-modal common representations loss:
$$ \mathcal{L}_{com} = \sum_i (1 - \mathcal{C}_{cii})^2 + \lambda_c \cdot \sum_i \sum_{j \neq i} \mathcal{C}_{cij}^2 $$where \( \lambda_c \) is a positive constant trading off the importance of the first invariance term (to make the common embeddings invariant to the input modalities) and the second redundancy reduction term (to decorrelate the embedding vector components and avoid model collapse).
Modality-unique representations loss:
$$ \mathcal{L}_{uni} = \sum_i \mathcal{C}_{uii}^2 + \lambda_u \cdot \sum_i \sum_{j \neq i} \mathcal{C}_{uij}^2 $$where \( \lambda_u \) is a positive constant trading off the importance of the first decorrelation term (to decorrelate different modalities) and the second redundancy reduction term (to decorrelate the embedding vector components).
Intra-Modal Representation Enhancement
To avoid the collapse of the decoupled unique dimensions in the cross-modal training, as well as to boost intra-modal representations, intra-modal training that covers all the embedding dimensions is introduced. For each modality, a cross-correlation matrix \( \mathcal{C}_{M1} \) (or \( \mathcal{C}_{M2} \)) is generated from the full dimensions of the embedding vectors \( Z_{M1}' \) and \( Z_{M1}'' \) (or \( Z_{M2}' \) and \( Z_{M2}'' \)).
Intra-modal losses:
$$ \mathcal{L}_{M1} = \sum_i (1 - \mathcal{C}_{\text{M1}ii})^2 + \lambda_{M1} \cdot \sum_i \sum_{j \neq i} \mathcal{C}_{\text{M1}ij}^2 $$ $$ \mathcal{L}_{M2} = \sum_i (1 - \mathcal{C}_{\text{M2}ii})^2 + \lambda_{M2} \cdot \sum_i \sum_{j \neq i} \mathcal{C}_{\text{M2}ij}^2 $$where \( \lambda_{M1} \) and \( \lambda_{M2} \) are positive constants trading off the importance of the invariance term and the redundancy reduction term.
Overall Training Objective
Combining the cross-modal common and unique losses, and the intra-modal losses, the overall training objective of DeCUR reads:
$$ \mathcal{L} = \mathcal{L}_{com} + \mathcal{L}_{uni} + \mathcal{L}_{M1} + \mathcal{L}_{M2} $$Deformable Attention for Modality-Informative Features
Apart from the DeCUR loss design, deformable attention is adopted to help ConvNet models focus on modality-informative regions. The deformable attention module was proposed in DAT and DAT++ to efficiently model the relations among feature tokens under the guidance of the important regions in the feature maps. Given an input feature map \( x \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times W \times C} \), a downsampled grid of points \( p \in \mathbb{R}^{H_G \times W_G \times 2} \) is generated as references, where \( H_G = H/r \) with \( r \) being the downscaling ratio. The query tokens \( q \) are fed into a lightweight sub-network \( \theta_{\text{offset}} \) to generate the offsets \( \Delta p \in \mathbb{R}^{H_G \times W_G \times 2} \) in order to get final deformed points with \( p + \Delta p \). Then the features are sampled from \( x \) at the locations of deformed points and interpolated to a feature map \( \bar{x} \in \mathbb{R}^{H_G \times W_G \times C} \). This sampled feature map \( \bar{x} \) is projected to keys \( k \) and values \( v \), where \( k = \bar{x}W_k \) and \( v = \bar{x}W_v \). Softmax attention is then calculated on flattened queries \( q \) and keys \( k \) and multiplied with values \( v \). The final output is reshaped back to the same size as the input feature map \( x \).
The deformable attention module is adopted in the last two stages of the encoder to learn regional focus while keeping efficiency. A residual connection from the input feature map to the output of the deformable attention module is added to restrict unexpected influences of the attention module, such as biasing the pretraining towards the pretext task by selecting unexpected deformable points.
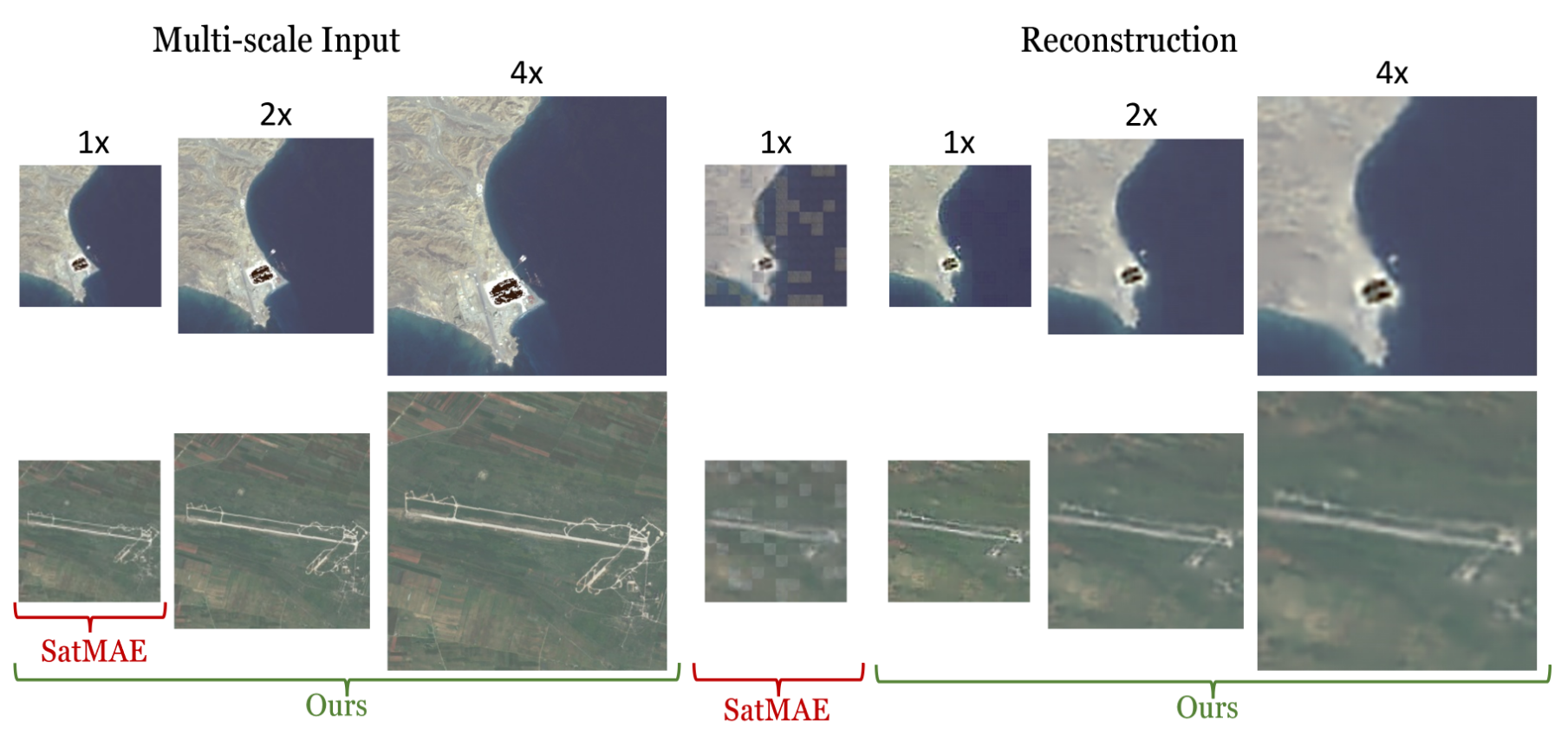
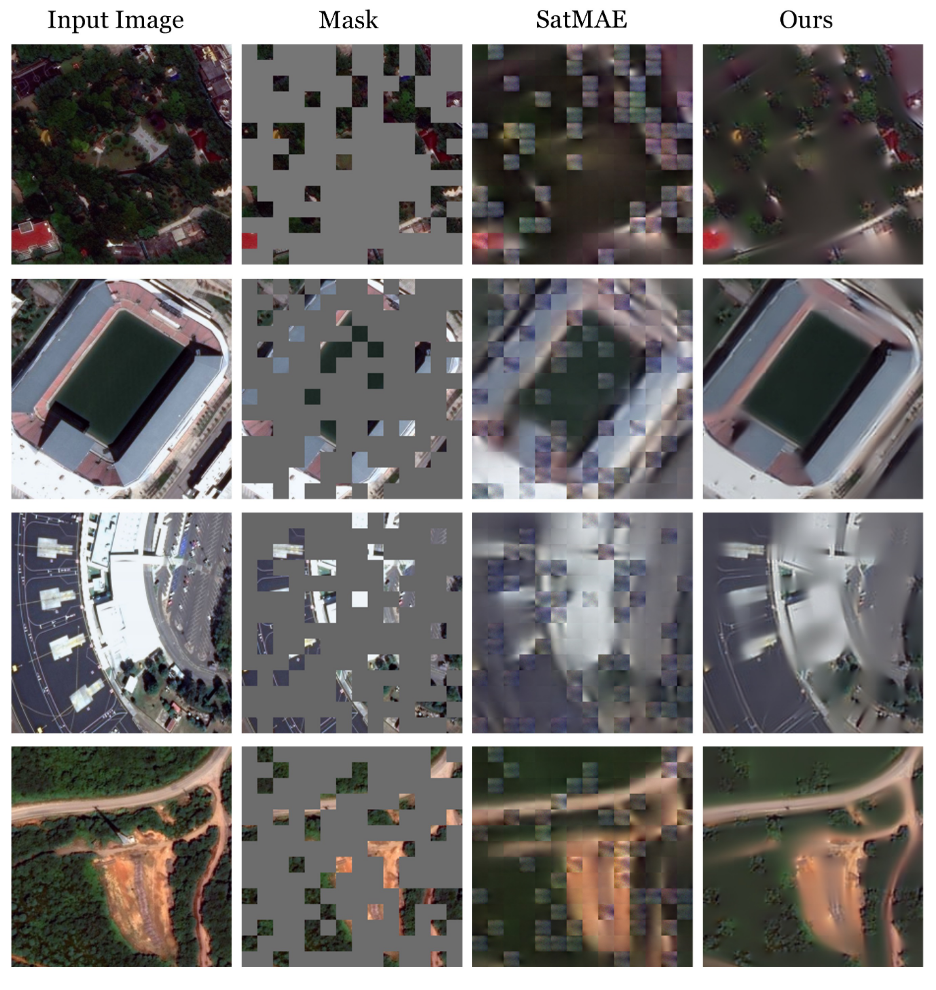
2. Masked Autoencoder (MAE)

Adoption in Remote Sensing:
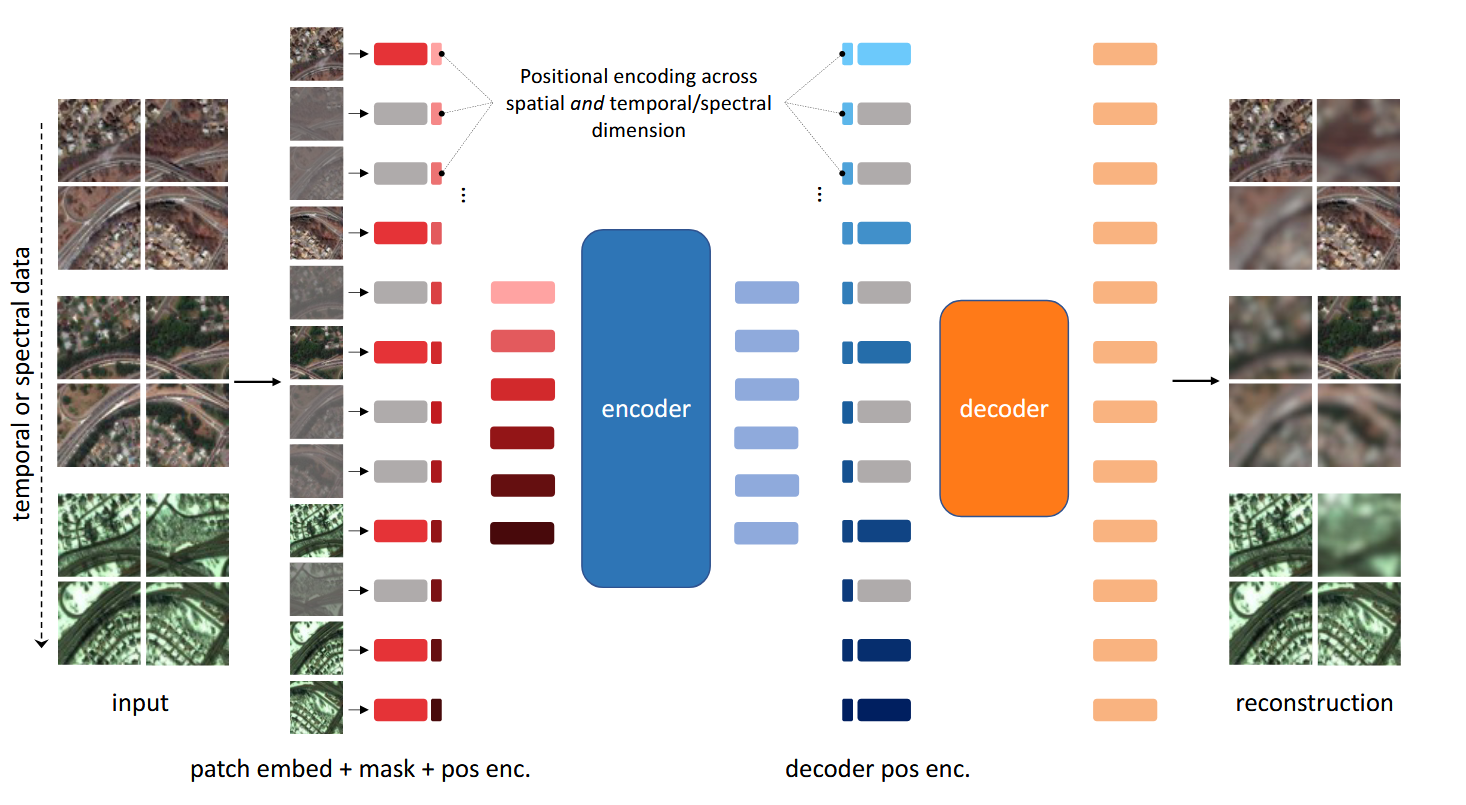
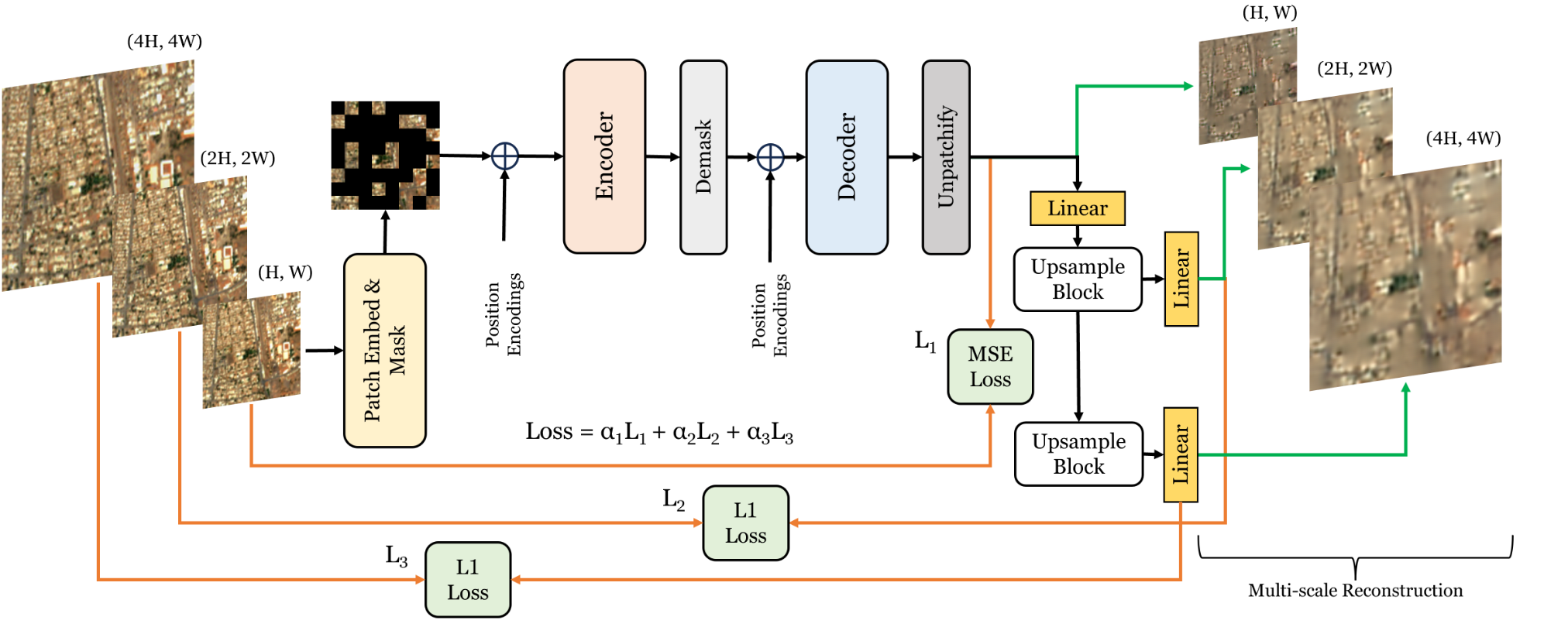
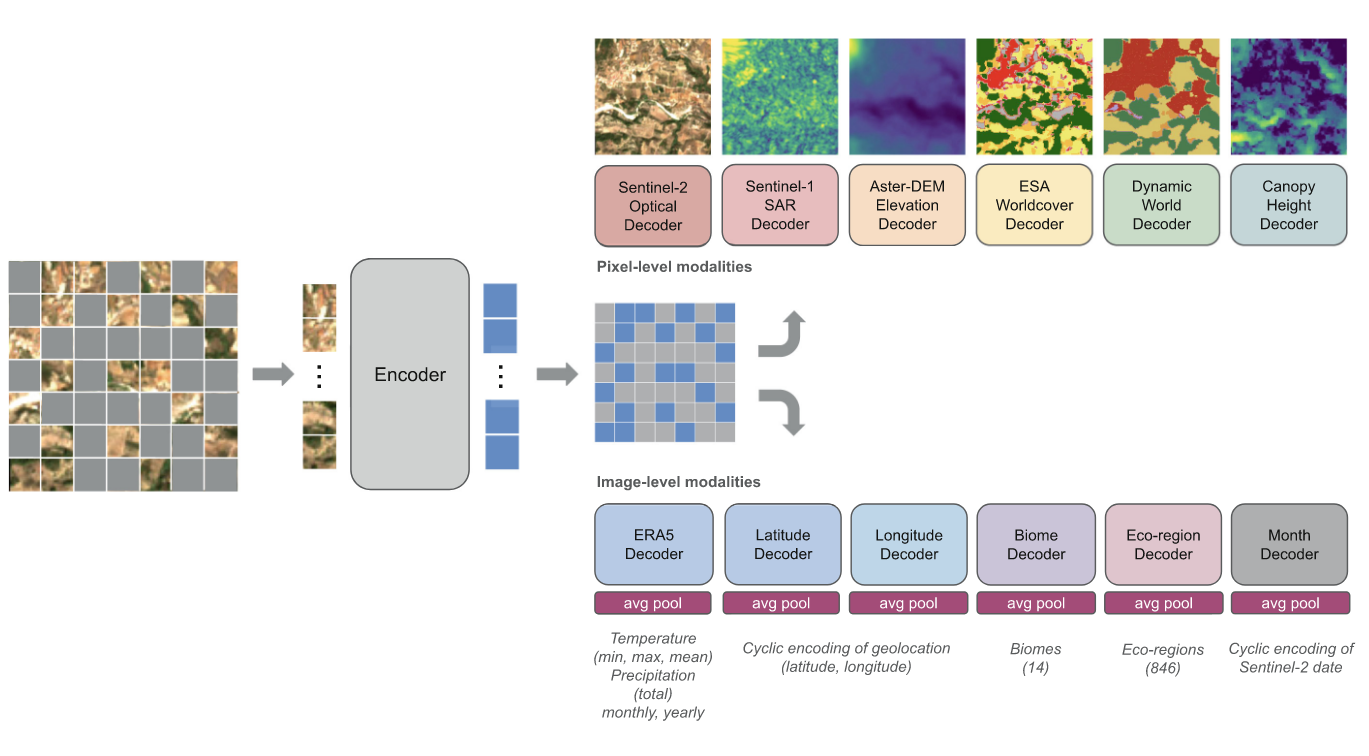
- Models: SatMAE [Cong et al., 2022], SatMAE++ [Noman et al., 2024], CROMA [Fuller et al., 2023], MMEarth [Nedungadi et al., 2024], DOFA [Xiong et al., 2025].


3. I-JEPA Style
Background (General Domain):
- Representative works: I-JEPA [Assran et al., 2023]
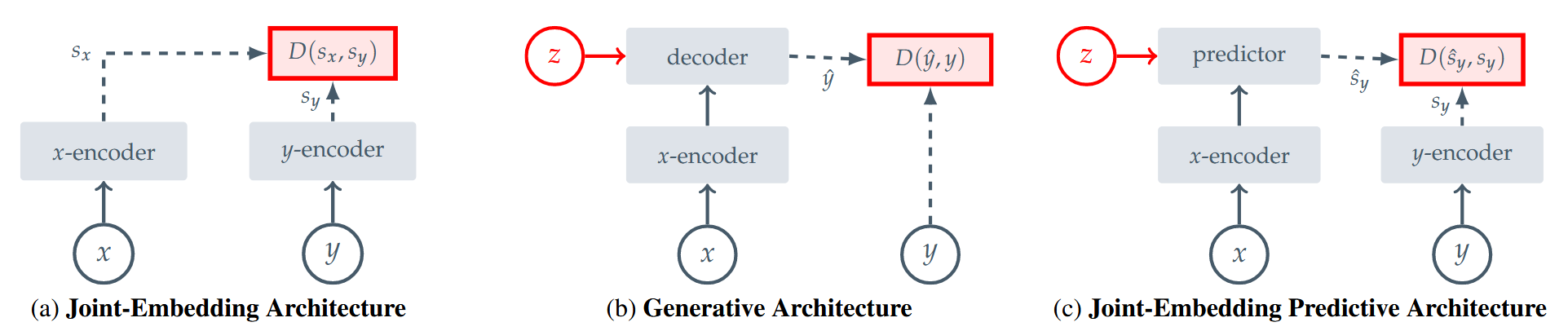
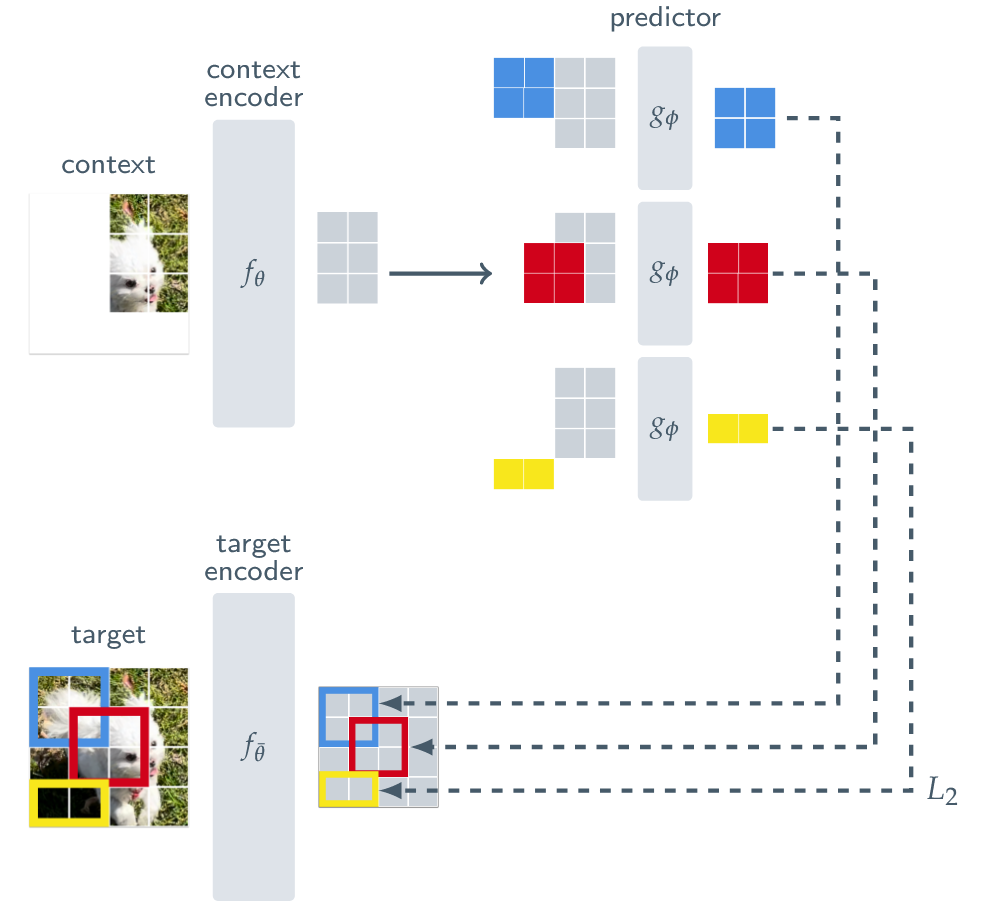
Embedding Predictive Architecture uses a single context block to predict the representations of various target blocks originating from the same image. The context encoder is a Vision Transformer (ViT), which only processes the visible context patches. The predictor is a narrow ViT that takes the context encoder output and, conditioned on positional tokens (shown in color), predicts the representations of a target block at a specific location. The target representations correspond to the outputs of the target-encoder, the weights of which are updated at each iteration via an exponential moving average of the context encoder weights
Adoption in Remote Sensing:
- Models: AnySat [Astruc et al., 2025].
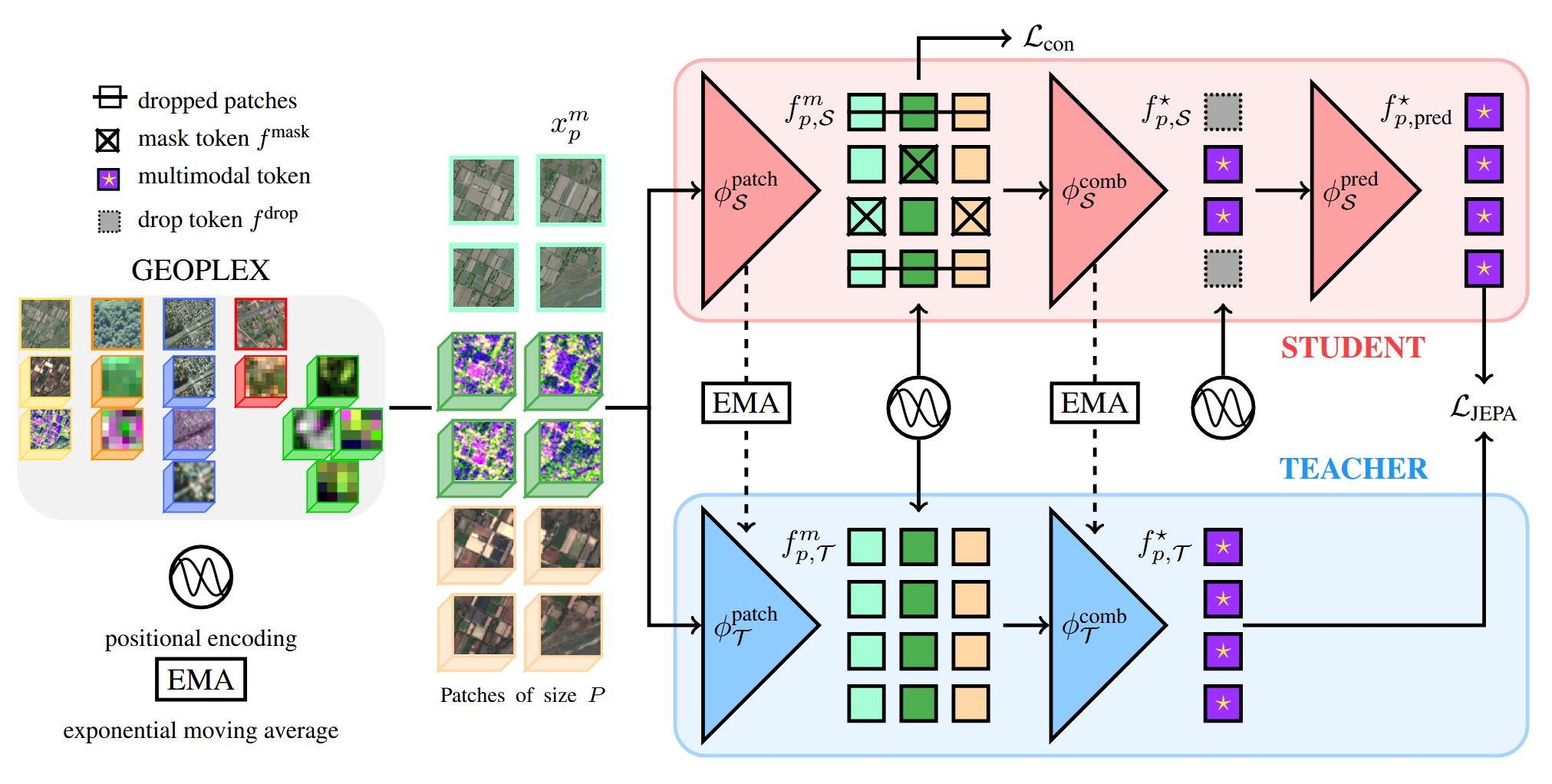
4. Latent Masked Image Modeling

5. Galileo (Current SOTA)
- Source: Galileo [Tseng et al., 2025].
- Key Features:
- Highly multimodal transformer to represent many remote sensing modalities.
- Novel self-supervised learning algorithm extracting multi-scale features across a flexible set of input modalities through mask modeling.
- Dual global and local contrastive losses which differ in their targets and masking strategies.

Other SSL Techniques
- DINO [Caron et al., 2021] / DINOv2 [Oquab et al., 2024] / DINOv3 [Siméoni et al., 2025]: Self-distillation with no labels using Vision Transformers. DINO learns visual features through a self-supervised teacher-student framework. DINOv2 improves robustness and scalability for larger models and datasets, while DINOv3 introduces further architectural and training optimizations. Adoption in Remote Sensing: DINO was adapted for joint SAR-optical representation learning using Vision Transformers [Wang et al., 2022b].
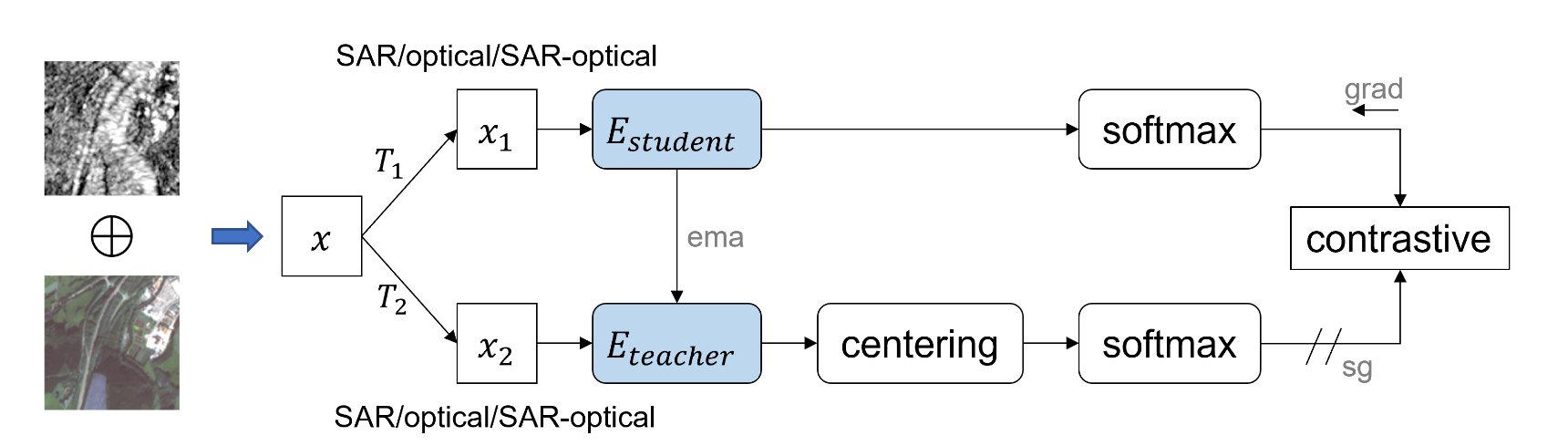
- iBOT [Zhou et al., 2022]: Image BERT pre-training with online tokenizer. iBOT combines masked image modeling with self-distillation, using an online tokenizer to generate supervision signals for masked patch prediction. Adoption in Remote Sensing: iBOT was adapted for remote sensing by pre-training on the Million-AID dataset, showing significant improvements in scene classification and other downstream tasks [Dimitrovski et al., 2024].
Other Remote Sensing Foundation Models
There are also some related works that introduce remote sensing foundation models:
- SoftCON [Wang et al., 2024b] / Satlas [Bastani et al., 2023]
- Prithvi-EO-2.0 [Szwarcman et al., 2025]
- RS-vHeat [Hu et al., 2025]
- SkySense Series: SkySense [Guo et al., 2024], SkySense v2 [Zhang et al., 2025], SkySense-O [Zhu et al., 2025], SkySense++ [Wu et al., 2025]
- GFM [Mendieta et al., 2023]
- MA3E [Chen et al., 2024c]
- CaCo [Mall et al., 2023]
- AlphaEarth [Brown et al., 2025]
Adaptation to Downstream Tasks
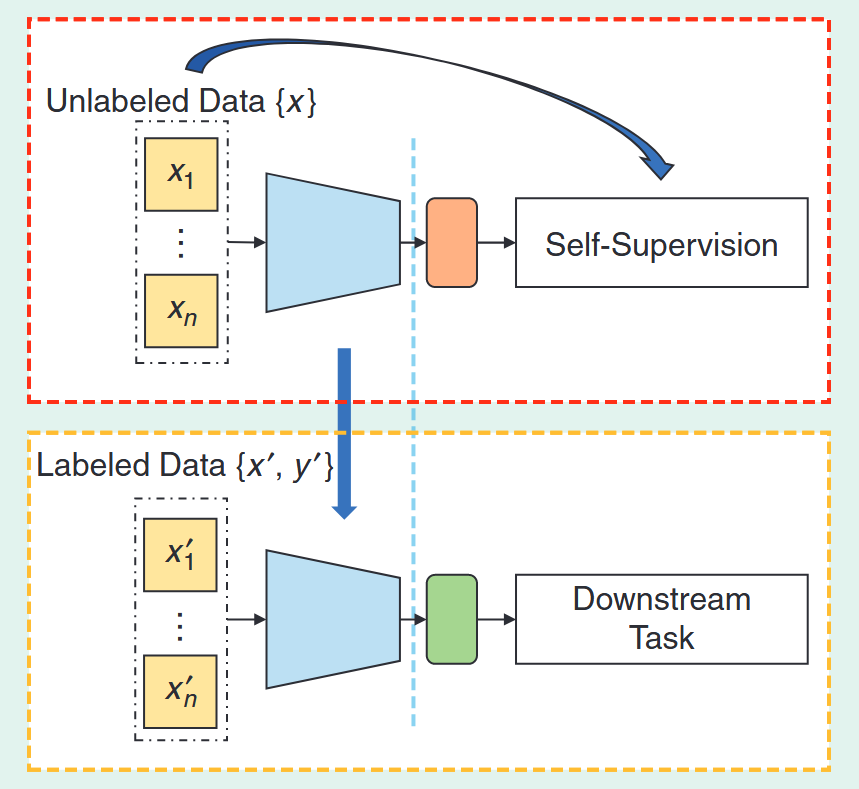
For a more in-depth exploration of self-supervised learning, readers are encouraged to consult several excellent surveys. A general overview of SSL algorithms and applications can be found in [Gui et al., 2024], while [Wang et al., 2022] and [Bai et al., 2025] provide comprehensive reviews specifically for remote sensing. Additionally, [Zong et al., 2025] explores the broader landscape of self-supervised multimodal learning.
References
-
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Norouzi, M., & Hinton, G. (2020). A Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Visual Representations. In International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML).
-
Radford, A., Kim, J. W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., Sastry, G., Askell, A., Mishkin, P., Clark, J., Krueger, G., & Sutskever, I. (2021). Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML).
-
Zbontar, J., Jing, L., Misra, I., LeCun, Y., & Deny, S. (2021). Barlow Twins: Self-Supervised Learning via Redundancy Reduction. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML).
-
Fuller, A., Millard, K., & Green, J. (2023). CROMA: Remote Sensing Representations with Contrastive Radar-Optical Masked Autoencoders. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS).
-
Wang, Y., Albrecht, C. M., Braham, N. A. A., Liu, C., Xiong, Z., & Zhu, X. X. (2024a). Decoupling Common and Unique Representations for Multimodal Self-supervised Learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).
-
Astruc, G., Gonthier, N., Mallet, C., & Landrieu, L. (2025). AnySat: One Earth Observation Model for Many Resolutions, Scales, and Modalities. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
-
He, K., Chen, X., Xie, S., Li, Y., Dollár, P., & Girshick, R. (2022). Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
-
Cong, Y., Khanna, S., Meng, C., Liu, P., Rozi, E., He, Y., Burke, M., Lobell, D., & Ermon, S. (2022). SatMAE: Pre-training Transformers for Temporal and Multi-Spectral Satellite Imagery. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS).
-
Noman, M., Naseer, M., Cholakkal, H., Anwer, R. M., Khan, S., & Khan, F. S. (2024). Rethinking Transformers Pre-Training for Multi-Spectral Satellite Imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
-
Xiong, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, F., Stewart, A. J., Hanna, J., Borth, D., Papoutsis, I., Saux, B. L., Camps-Valls, G., & Zhu, X. X. (2025). Neural Plasticity-Inspired Multimodal Foundation Model for Earth Observation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.15356.
-
Nedungadi, V., Kariryaa, A., Oehmcke, S., Belongie, S., Igel, C., & Lang, N. (2024). MMEarth: Exploring Multi-modal Pretext Tasks for Geospatial Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).
-
Assran, M., Duval, Q., Misra, I., Bojanowski, P., Vincent, P., Rabbat, M., LeCun, Y., & Ballas, N. (2023). Self-Supervised Learning from Images with a Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
-
Wei, Y., Gupta, A., & Morgado, P. (2024). Towards Latent Masked Image Modeling for Self-supervised Visual Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).
-
Tseng, G., Fuller, A., Reil, M., Herzog, H., Beukema, P., Bastani, F., Green, J. R., Shelhamer, E., Kerner, H., & Rolnick, D. (2025). Galileo: Learning Global & Local Features of Many Remote Sensing Modalities. In International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML).
-
Wang, Y., Albrecht, C. M., & Zhu, X. X. (2024b). Multilabel-Guided Soft Contrastive Learning for Efficient Earth Observation Pretraining. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 62, 1–16.
-
Bastani, F., Wolters, P., Gupta, R., Ferdinando, J., & Kembhavi, A. (2023). SatlasPretrain: A Large-Scale Dataset for Remote Sensing Image Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
-
Guo, X., Lao, J., Dang, B., Zhang, Y., Yu, L., Ru, L., Zhong, L., Huang, Z., Wu, K., Hu, D., He, H., Wang, J., Chen, J., Yang, M., Zhang, Y., & Li, Y. (2024). SkySense: A Multi-Modal Remote Sensing Foundation Model Towards Universal Interpretation for Earth Observation Imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
-
Zhang, Y., Ru, L., Wu, K., Yu, L., Liang, L., Li, Y., & Chen, J. (2025). SkySense V2: A Unified Foundation Model for Multi-modal Remote Sensing. In International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
-
Zhu, Q., Lao, J., Ji, D., Luo, J., Wu, K., Zhang, Y., Ru, L., Wang, J., Chen, J., Yang, M., Liu, D., & Zhao, F. (2025). SkySense-O: Towards Open-World Remote Sensing Interpretation with Vision-Centric Visual-Language Modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
-
Wu, K., Zhang, Y., Ru, L., Dang, B., Lao, J., Yu, L., Luo, J., Zhu, Z., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Zhu, Q., Wang, J., Yang, Ming, Chen, J., Zhang, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). A Semantic-Enhanced Multi-Modal Remote Sensing Foundation Model for Earth Observation. Nature Machine Intelligence, 7(8), 1235–1249.
-
Szwarcman, D., Roy, S., Fraccaro, P., Gíslason, Þ. E., Blumenstiel, B., Ghosal, R., de Oliveira, P. H., Almeida, J. L. d. S., Sedona, R., Kang, Y., Chakraborty, S., Wang, S., Gomes, C., Kumar, A., Truong, M., Godwin, D., Lee, H., Hsu, C.-Y., Asanjan, A. A., Mujeci, B., Shidham, D., Keenan, T., Arevalo, P., Li, W., Alemohammad, H., Olofsson, P., Hain, C., Kennedy, R., Zadrozny, B., Bell, D., Cavallaro, G., Watson, C., Maskey, M., Ramachandran, R., & Moreno, J. B. (2025). Prithvi-EO-2.0: A Versatile Multi-Temporal Foundation Model for Earth Observation Applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.02732.
-
Mendieta, M., Han, B., Shi, X., Zhu, Y., & Chen, C. (2023). Towards Geospatial Foundation Models via Continual Pretraining. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
-
Chen, B., Chen, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, Y., & Li, X. (2024c). Masked Angle-Aware Autoencoder for Remote Sensing Images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).
-
Mall, U., Hariharan, B., & Bala, K. (2023). Change-Aware Sampling and Contrastive Learning for Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
-
Hu, H., Wang, P., Bi, H., Tong, B., Wang, Z., Diao, W., Chang, H., Feng, Y., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Ye, Q., Fu, K., & Sun, X. (2025). RS-vHeat: Heat Conduction Guided Efficient Remote Sensing Foundation Model. In International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
-
Rolf, E., Klemmer, K., Robinson, C., & Kerner, H. (2024). Position: Mission Critical – Satellite Data Is a Distinct Modality in Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML).
-
Brown, C. F., Kazmierski, M. R., Pasquarella, V. J., Rucklidge, W. J., Samsikova, M., Zhang, C., Shelhamer, E., Lahera, E., Wiles, O., Ilyushchenko, S., Gorelick, N., Zhang, L. L., Alj, S., Schechter, E., Askay, S., Guinan, O., Moore, R., Boukouvalas, A., & Kohli, P. (2025). AlphaEarth Foundations: An Embedding Field Model for Accurate and Efficient Global Mapping from Sparse Label Data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2507.22291.
-
Liu, F., Chen, D., Guan, Z., Zhou, X., Zhu, J., Ye, Q., Fu, L., & Zhou, J. (2024). RemoteCLIP: A Vision Language Foundation Model for Remote Sensing. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 62, 1–16.
-
Caron, M., Touvron, H., Misra, I., Jégou, H., Mairal, J., Bojanowski, P., & Joulin, A. (2021). Emerging Properties in Self-Supervised Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).
-
Chen, T., Kornblith, S., Swersky, K., Norouzi, M., & Hinton, G. E. (2020). Big Self-Supervised Models Are Strong Semi-Supervised Learners. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS).
-
Grill, J.-B., Strub, F., Altché, F., Tallec, C., Richemond, P., Buchatskaya, E., Doersch, C., Avila Pires, B., Guo, Z., Gheshlaghi Azar, M., Piot, B., Kavukcuoglu, K., Munos, R., & Valko, M. (2020). Bootstrap Your Own Latent: A New Approach to Self-Supervised Learning. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS).
-
Zhou, J., Wei, C., Wang, H., Shen, W., Xie, C., Yuille, A., & Kong, T. (2022). iBOT: Image BERT Pre-training with Online Tokenizer. In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR).
-
Oquab, M., Darcet, T., Moutakanni, T., Vo, H. V., Szafraniec, M., Khalidov, V., Fernandez, P., Haziza, D., Massa, F., & El-Nouby, A. (2024). DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision. Transactions on Machine Learning Research.
-
Siméoni, O., Vo, H. V., Seitzer, M., Baldassarre, F., Oquab, M., Jose, C., Khalidov, V., Szafraniec, M., Yi, S., Ramamonjisoa, M., Massa, F., Haziza, D., Wehrstedt, L., Wang, J., Darcet, T., Moutakanni, T., Sentana, L., Roberts, C., Vedaldi, A., Tolan, J., Brandt, J., Couprie, C., Mairal, J., Jégou, H., Labatut, P., & Bojanowski, P. (2025). DINOv3. arXiv preprint arXiv:2508.10104.
-
Wang, Y., Albrecht, C. M., Braham, N. A. A., Mou, L., & Zhu, X. X. (2022). Self-Supervised Learning in Remote Sensing: A Review. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 10(4), 213–247.
-
Gui, J., Chen, T., Zhang, J., Cao, Q., Sun, Z., Luo, H., & Tao, D. (2024). A Survey on Self-Supervised Learning: Algorithms, Applications, and Future Trends. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 46(12), 9052–9071.
-
Zong, Y., Aodha, O. M., & Hospedales, T. M. (2025). Self-Supervised Multimodal Learning: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 47(7), 5299–5318.
-
Bai, L., Zhang, X., Qin, W., Long, J., Wang, H., Dong, X., & Du, S. (2025). From Orbit to Ground: A Comprehensive Review of Multimodal Self-Supervised Learning for Remote Sensing. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 13(4), 346–381.
-
Wang, Y., Albrecht, C. M., & Zhu, X. X. (2022b). Self-Supervised Vision Transformers for Joint SAR-Optical Representation Learning. In IGARSS 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium.
-
Dimitrovski, I., Kitanovski, I., Simidjievski, N., & Kocev, D. (2024). In-Domain Self-Supervised Learning Improves Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 21, 1–5.